Orientation and Surfaces
The heart has been described by many texts as “a pyramid which has fallen over”. The apexof this pyramid pointing in an anterior-inferior direction.
In its typical anatomical orientation, the heart has 5 surfaces, formed by different internal divisions of the heart:
- Anterior (or sternocostal) – Right ventricle.
- Posterior (or base) – Left atrium.
- Inferior (or diaphragmatic) – Left and right ventricles.
- Right pulmonary – Right atrium.
- Left pulmonary – Left ventricle.
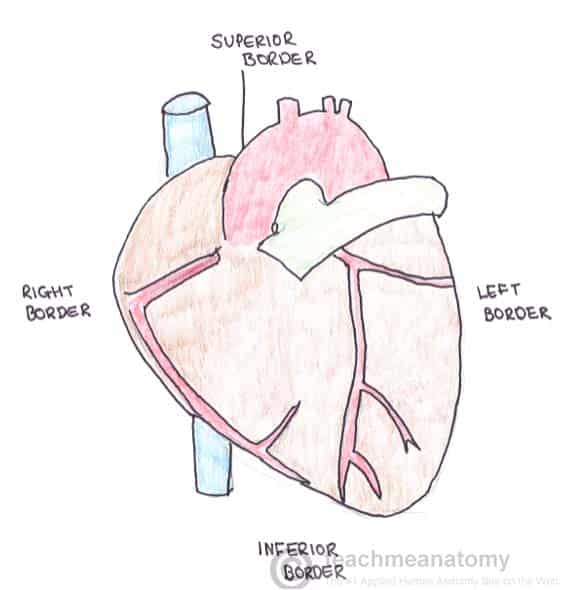
Borders
Separating the surfaces of the heart are its borders. There are four main borders of the heart:
- Right border – Right atrium
- Inferior border – Left ventricle and right ventricle
- Left border – Left ventricle (and some of the left atrium)
- Superior border – Right and left atrium and the great vessels
Sulci of the Heart
The heart is a hollow structure. On the interior, it is divided into four chambers. These divisions create grooves on the surface of the heart – these are known as sulci.
The coronary sulcus (or atrioventricular groove) runs transversely around the heart – it represents the wall dividing the atria from the ventricles. The sinus contains important vasculature, such as the right coronary artery.
The anterior and posterior interventricular sulci can be found running vertically on their respective sides of the heart. They represent the wall separating the ventricles.
Pericardial Sinuses
The pericardial sinuses are not the same as ‘anatomical sinuses’ (such as the paranasal sinuses). They are passageways formed the unique way in which the pericardium folds around the great vessels.
- The oblique pericardial sinus is a blind ending passageway (‘cul de sac’) located on the posterior surface of the heart.
- The transverse pericardial sinus is found superiorly on the heart. It can be used in coronary artery bypass grafting – see below.
No comments:
Post a Comment